Performance is the primary determinant of user experience in the field of web development nowadays. A slow website or application can hurt search engine rankings, increase bounce rates, and irritate users. For JavaScript-dependent apps to operate at their best, advanced optimization techniques and patterns must be used. This article discusses ten advanced JavaScript performance optimization techniques and patterns that may help developers write faster and more efficient code. Each method is shown with examples to demonstrate its effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
Read Also: What are the key topics you will learn from the JavaScript syllabus?
Introduction

JavaScript serves as the foundation for modern web applications. Although JavaScript is a powerful script, its adaptability can result in inefficiencies if used irresponsibly. As online programs get more complex, JavaScript optimization becomes essential to maintaining responsive and fast systems. This article covers sophisticated techniques to improve JavaScript performance, which will enable you to reduce runtime, use less memory, and provide users a more seamless experience.
1. Reduce DOM Manipulation and Access
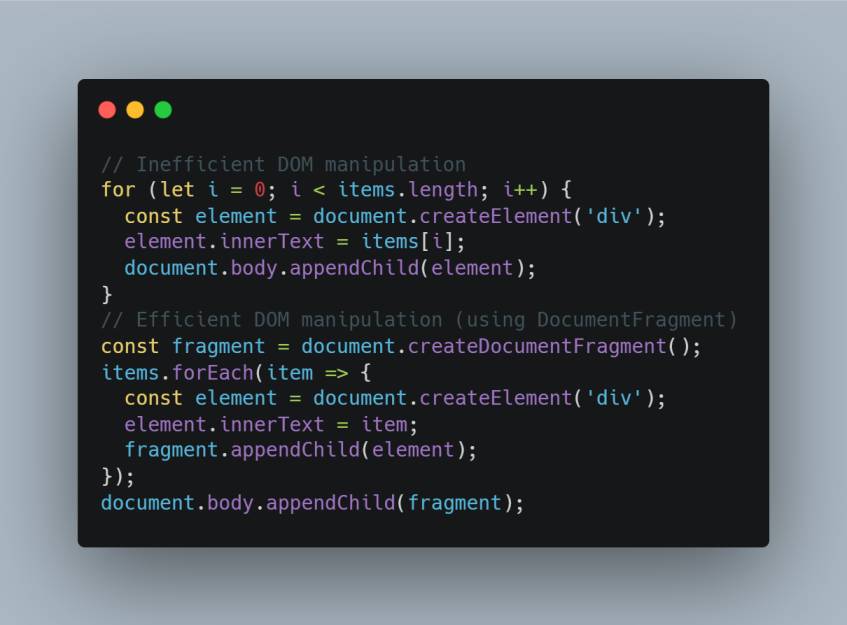
One of the most costly JavaScript activities is accessing and modifying the DOM. The browser has to recalculate layouts, repaint the page, and sometimes re-render items each time you work with the DOM. Reducing the quantity of DOM access operations and batching them wherever feasible are crucial for enhancing performance.
Why Does DOM Access Cost So Much?
Must Know: What are the top 10 JavaScript concepts programmers should know to excel in web development?
Methods of Optimization
Example of Code:
2. Make Use of Effective Iterators and Loops
Although they are essential to JavaScript, loops are not all made equal. Performance may be greatly impacted by selecting the appropriate loop structure, particularly when working with big data sets.
Top Techniques for Loops
Use Contemporary Iterators: Choose contemporary techniques like forEach(), map(), filter(), and reduce() over more antiquated for or while loops. These techniques provide clearer code and are internally optimized.
Steer clear of unnecessary looping: If you find yourself going over the data repeatedly, think about restructuring to cut down on the number of passes.
Example of Code:

3. Discourage and Stop Expensive Activities
If you do costly calculations or DOM transformations in response to each event, event listeners (such as resize, scroll, or keyup) might cause performance bottlenecks. Two popular techniques to restrict how many times a function is called in a certain amount of time are debouncing and throttling.
The function is run after a certain amount of time after the last event trigger thanks to debouncing.
Example of Code:

4. Prevent Memory Losses and Enhance Trash Collection
When objects in JavaScript are no longer required but are still stored in memory, this is known as a memory leak. In addition to increasing memory use, this hinders trash collection, which eventually degrades performance. Maintaining JavaScript's performance requires effective memory management.
Typical Memory Leak Sources:
Event listeners linked to later-removed items are known as uneared event listeners.
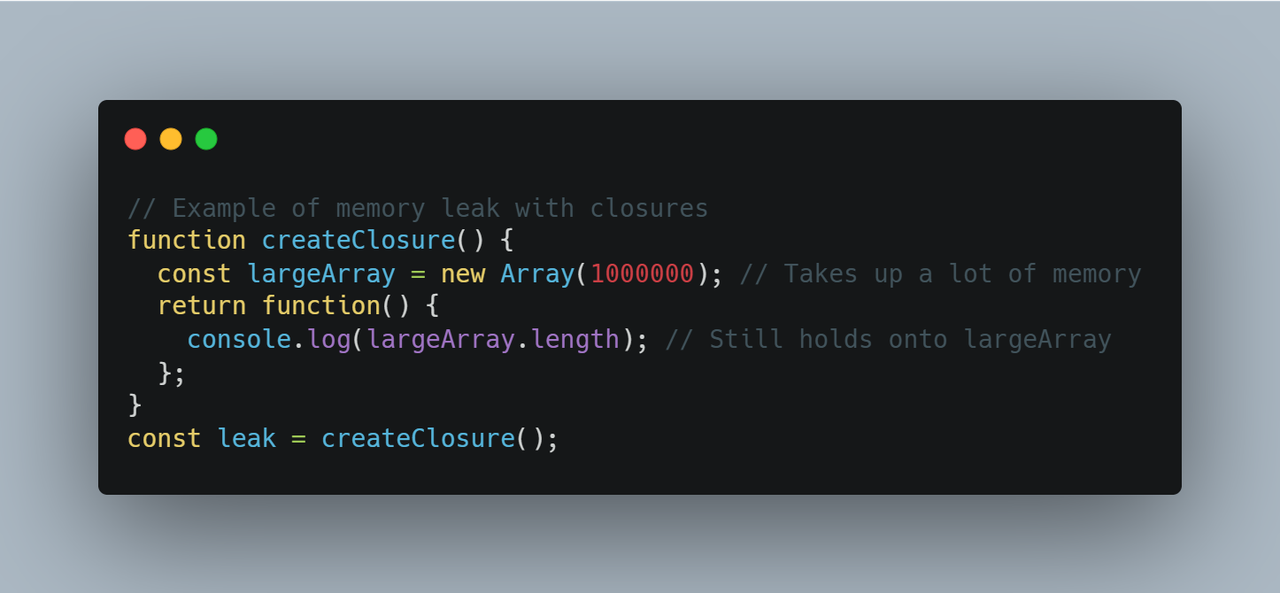
When a function retains references to variables after the outer function has returned, this is known as a closure.
Items that make references to one another in a way that hinders trash collection are known as circular references.
An example of code (memory leak):
5. JavaScript and Assets Load Lazy
By delaying the loading of non-essential resources until they are required, lazy loading enhances performance and initial load time. Large JavaScript packages, pictures, and other materials benefit greatly from this.
Methods for Slow Loading:
Example of Dynamic Import Code:

6. Use Web Workers to Perform Complex Calculations
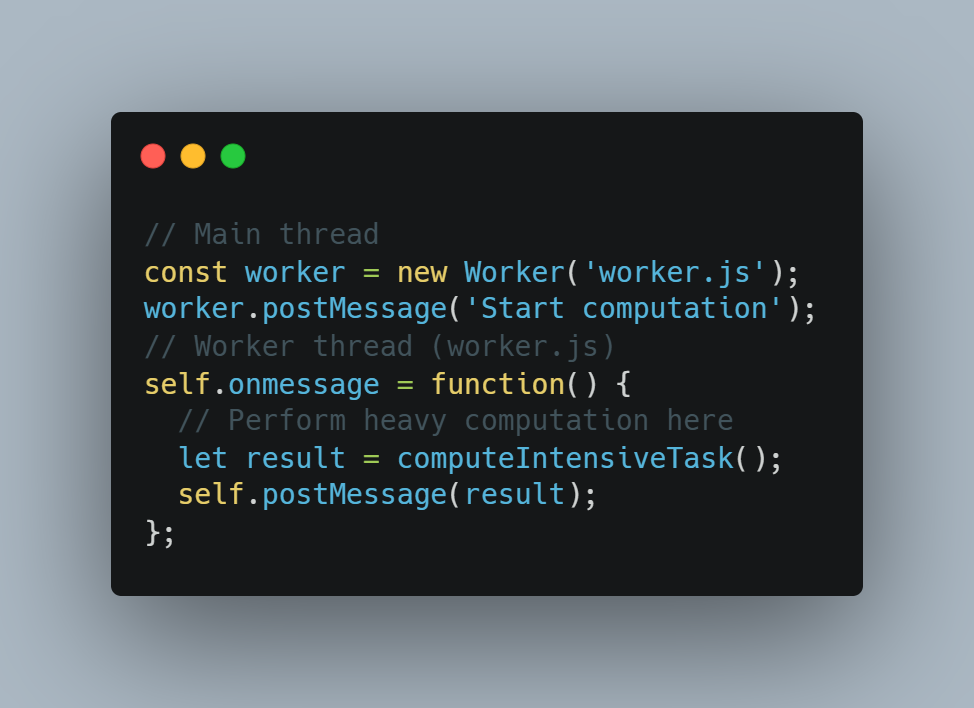
Because JavaScript is by default single-threaded, lengthy processes may block the main thread and render the user interface unusable. By shifting complex calculations to a different thread, web workers help you increase speed and maintain a responsive user interface.
Example of Code:
7. Make API requests more efficient and cached
Your application may become slower and take longer to load if you make frequent or superfluous API requests. Performance may be improved by caching API replies and reducing duplicate network queries, particularly in Single Page Applications (SPAs).
Example of Code:

8. Effective Closure Use
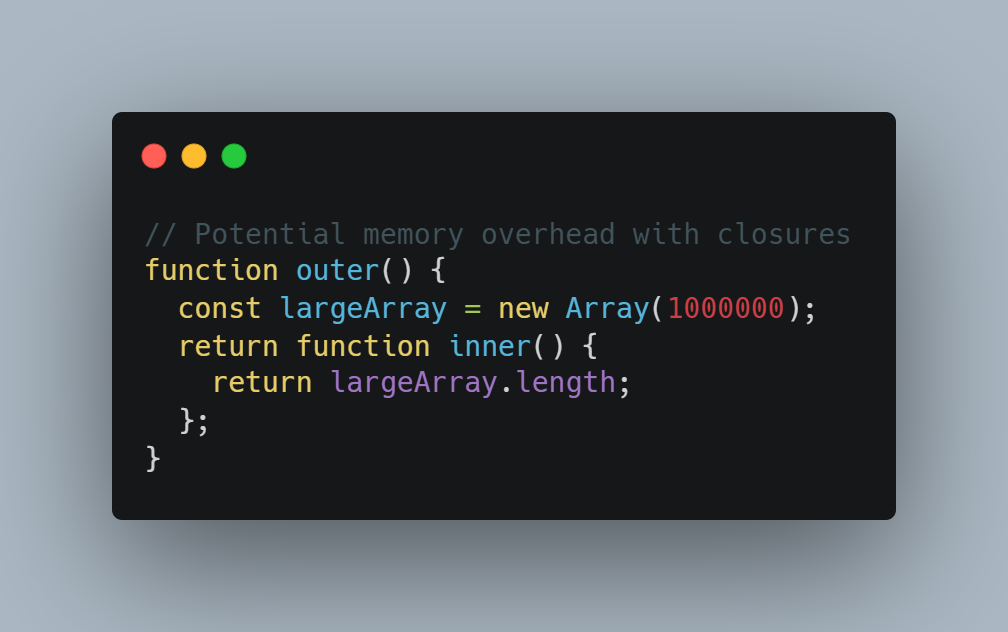
JavaScript closures are strong, but if they are utilized improperly, they can quickly cause performance problems. If closures are not handled appropriately, they may result in memory overhead since they keep references to their outside scope.
Example of Code:
9. Use RequestAnimationFrame to Improve Rendering
RequestAnimationFrame is a more effective option than setTimeout or setInterval when handling frequent UI changes or creating animations. It contributes to greater performance and smoother animations by ensuring that updates are in sync with the browser's refresh rate.
Example of Code:

10. Employ Data Structures That Are Immutable
Every time a modification is performed, immutable data structures make sure that the data is not altered directly but rather returns a new object. By preventing unforeseen side effects and enabling more effective change detection in frameworks like React, this can improve speed.
Example of Code:

In conclusion
JavaScript speed optimization is a continuous effort that necessitates careful thought about the organization and execution of code. You can make sure your JavaScript apps are as responsive and effective as possible by adhering to these ten sophisticated strategies and patterns. Every strategy, from utilizing Web Workers to reducing DOM modifications, is essential for enhancing efficiency and providing a seamless user experience.
Performance is the primary determinant of user experience in the field of web development nowadays. A slow website or application can hurt search engine rankings, increase bounce rates, and irritate users. For JavaScript-dependent apps to operate at their best, advanced optimization techniques and patterns must be used. This article discusses ten advanced JavaScript performance optimization techniques and patterns that may help developers write faster and more efficient code. Each method is shown with examples to demonstrate its effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
Read Also: What are the key topics you will learn from the JavaScript syllabus?
Introduction
JavaScript serves as the foundation for modern web applications. Although JavaScript is a powerful script, its adaptability can result in inefficiencies if used irresponsibly. As online programs get more complex, JavaScript optimization becomes essential to maintaining responsive and fast systems. This article covers sophisticated techniques to improve JavaScript performance, which will enable you to reduce runtime, use less memory, and provide users a more seamless experience.
1. Reduce DOM Manipulation and Access
One of the most costly JavaScript activities is accessing and modifying the DOM. The browser has to recalculate layouts, repaint the page, and sometimes re-render items each time you work with the DOM. Reducing the quantity of DOM access operations and batching them wherever feasible are crucial for enhancing performance.
Why Does DOM Access Cost So Much?
Must Know: What are the top 10 JavaScript concepts programmers should know to excel in web development?
Methods of Optimization
Example of Code:
2. Make Use of Effective Iterators and Loops
Although they are essential to JavaScript, loops are not all made equal. Performance may be greatly impacted by selecting the appropriate loop structure, particularly when working with big data sets.
Top Techniques for Loops
Use Contemporary Iterators: Choose contemporary techniques like forEach(), map(), filter(), and reduce() over more antiquated for or while loops. These techniques provide clearer code and are internally optimized.
Steer clear of unnecessary looping: If you find yourself going over the data repeatedly, think about restructuring to cut down on the number of passes.
Example of Code:
3. Discourage and Stop Expensive Activities
If you do costly calculations or DOM transformations in response to each event, event listeners (such as resize, scroll, or keyup) might cause performance bottlenecks. Two popular techniques to restrict how many times a function is called in a certain amount of time are debouncing and throttling.
The function is run after a certain amount of time after the last event trigger thanks to debouncing.
Example of Code:
4. Prevent Memory Losses and Enhance Trash Collection
When objects in JavaScript are no longer required but are still stored in memory, this is known as a memory leak. In addition to increasing memory use, this hinders trash collection, which eventually degrades performance. Maintaining JavaScript's performance requires effective memory management.
Typical Memory Leak Sources:
Event listeners linked to later-removed items are known as uneared event listeners.
When a function retains references to variables after the outer function has returned, this is known as a closure.
Items that make references to one another in a way that hinders trash collection are known as circular references.
An example of code (memory leak):
5. JavaScript and Assets Load Lazy
By delaying the loading of non-essential resources until they are required, lazy loading enhances performance and initial load time. Large JavaScript packages, pictures, and other materials benefit greatly from this.
Methods for Slow Loading:
Example of Dynamic Import Code:
6. Use Web Workers to Perform Complex Calculations
Because JavaScript is by default single-threaded, lengthy processes may block the main thread and render the user interface unusable. By shifting complex calculations to a different thread, web workers help you increase speed and maintain a responsive user interface.
Example of Code:
7. Make API requests more efficient and cached
Your application may become slower and take longer to load if you make frequent or superfluous API requests. Performance may be improved by caching API replies and reducing duplicate network queries, particularly in Single Page Applications (SPAs).
Example of Code:
8. Effective Closure Use
JavaScript closures are strong, but if they are utilized improperly, they can quickly cause performance problems. If closures are not handled appropriately, they may result in memory overhead since they keep references to their outside scope.
Example of Code:
9. Use RequestAnimationFrame to Improve Rendering
RequestAnimationFrame is a more effective option than setTimeout or setInterval when handling frequent UI changes or creating animations. It contributes to greater performance and smoother animations by ensuring that updates are in sync with the browser's refresh rate.
Example of Code:
10. Employ Data Structures That Are Immutable
Every time a modification is performed, immutable data structures make sure that the data is not altered directly but rather returns a new object. By preventing unforeseen side effects and enabling more effective change detection in frameworks like React, this can improve speed.
Example of Code:
In conclusion
JavaScript speed optimization is a continuous effort that necessitates careful thought about the organization and execution of code. You can make sure your JavaScript apps are as responsive and effective as possible by adhering to these ten sophisticated strategies and patterns. Every strategy, from utilizing Web Workers to reducing DOM modifications, is essential for enhancing efficiency and providing a seamless user experience.